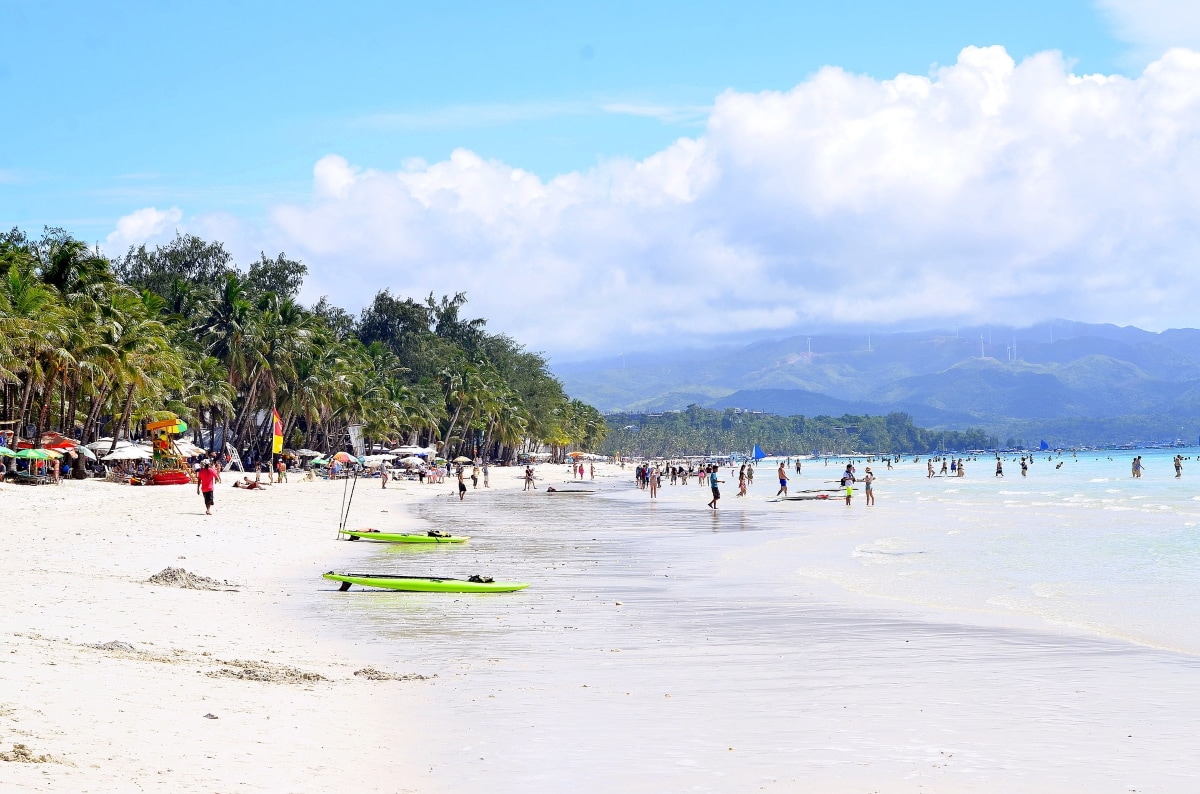
Philippine Economy
The economy of the Philippines is the third-largest in Southeast Asia. It has transitioned from an agriculturally-based to a manufacturing-driven economy, making the Philippines a newly industrialised country.
The country is one of the emerging markets and is the sixth richest in ASEAN in terms of GDP per capita, which reached $3,099 in 2018. Its GDP has sustainably grown over 7% annually since 2012. Last year, the economy grew by 6.5% with a nominal GDP of $331 billion. The IMF forecasts the Filipino GDP to increase by over 50% in the next five years, to reach $510 billion in 2023.
Filipino economy dominated by a young population
The population of the Philippines has almost doubled in a 30-year span, reaching 107 million in 2018. It has increased by an average of 1.61% annually for the last decade. Only 5% of the population is over 65 years of age, while one-third of the population is 14 years old or younger.
As for the unemployment rate, around 5.5% of the population were jobless last year. Overpopulation – due to the rapid growth of the population – is one of the main reasons for the unemployment rate.

The Filipino peso (₱) is the official currency of the Philippines. At present, the Philippines applies a freely floating exchange rate system for its currency.
Monetary policies in the Philippines are determined by its central bank, Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, established on 3 July 1993. Bangko Sentral’s main functions are to maintain price stability, manage liquidity, and issue the national currency.
In 2018, the inflation target of the Philippines was set to be between 2% and 4%. However, it jumped to 5.2% last year, exceeding the target. The IMF predicts the country’s inflation rate will decrease to 3.7% in 2019.

As a newly-industrialised country, the services sector dominates the economy of the Philippines and contributes to over 58% of the nation’s GDP. Meanwhile, industry and the agricultural sector account for 34% and 7% of GDP respectively.
Major industries in the Philippines include electronics assembly, business process outsourcing, food manufacturing, shipbuilding, chemicals, textiles, and petroleum refining. In agriculture, the Philippines is one of the world’s largest producers of coconuts and pineapples.
Filipino Economy: Trade and Competitiveness
For the last three decades, the Philippines’ trade balance has consistently remained negative. In 2018, the Philippines posted a record trade deficit of $41.44 billion. Merchandise exports declined 1.8 percent to $67.488 billion, imports rose 13.4 percent to $108.928 billion.
The Philippines’ primary export partners are East Asian countries, with 41% of all exports going to Japan, Hong Kong and China. Its major import partners are China, Japan, and ASEAN countries, such as Thailand, Singapore and Indonesia.
In recent years, FDI inflows to the Philippines have been rising progressively. In 2017, FDI inflows to the Philippines hit an all-time high of $9.5 billion, surpassing the central bank target of $8 billion. Japan, the U.S., and Singapore are the main investors, while inflows are concentrated in the manufacturing and the real estate sector. For 2019, the central bank is targeting an FDI inflow of $10.2 billion.
In the ease of doing business ranking, the World Bank put the Philippines at 124th position due to inadequate infrastructure, high power costs, tax regulations, and foreign ownership restrictions.
Stock exchanges and capital markets
The Philippine Stock Exchange (PSE), headquartered in Manila, is the national stock exchange of the Philippines. It was a merger between the Manila Stock Exchange and the Makati Stock Exchange in 1992. The stock exchange had 323 listed companies in 2018, with a total market cap of $253 billion. PSE categorised the listed companies based on market cap under the First Board, Second Board or the Small and Medium Enterprises Board.
The main index is the PSE Composite Index (PSEi) composed of the top 30 listed companies. There are also six additional sector-based indices: PSE Financials Index (FIN), PSE Holding Firms Index (HDG), PSE Industrial Index (IND), PSE Mining and Oil Index (M-O), PSE Property Index (PRO), PSE Services Index (SVC) and PSE Total Returns Index (TRI).
Philippines: Investment Regulation
Liberalisation of business practises in the Philippines has opened up more areas for investment, granting foreign investors the same incentives as other ASEAN members. There is no requirement for foreign investors who want to invest in shares and fixed income products in the Philippines. However, foreign investments have to be registered at the Bangko Sentral. The general foreign ownership limit (FOL) is 40%.
A few sectors, such as mass media, retail, advertising, public services, small-scale mining, private security, and utilisation of marine resources, are exclusively reserved for its citizens. The Regular Foreign Investment Negative List is published by the Philippines government and regularly updated.










 Australia
Australia China
China India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Japan
Japan Malaysia
Malaysia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Germany
Germany Hong Kong
Hong Kong USA
USA Switzerland
Switzerland Singapore
Singapore
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom










