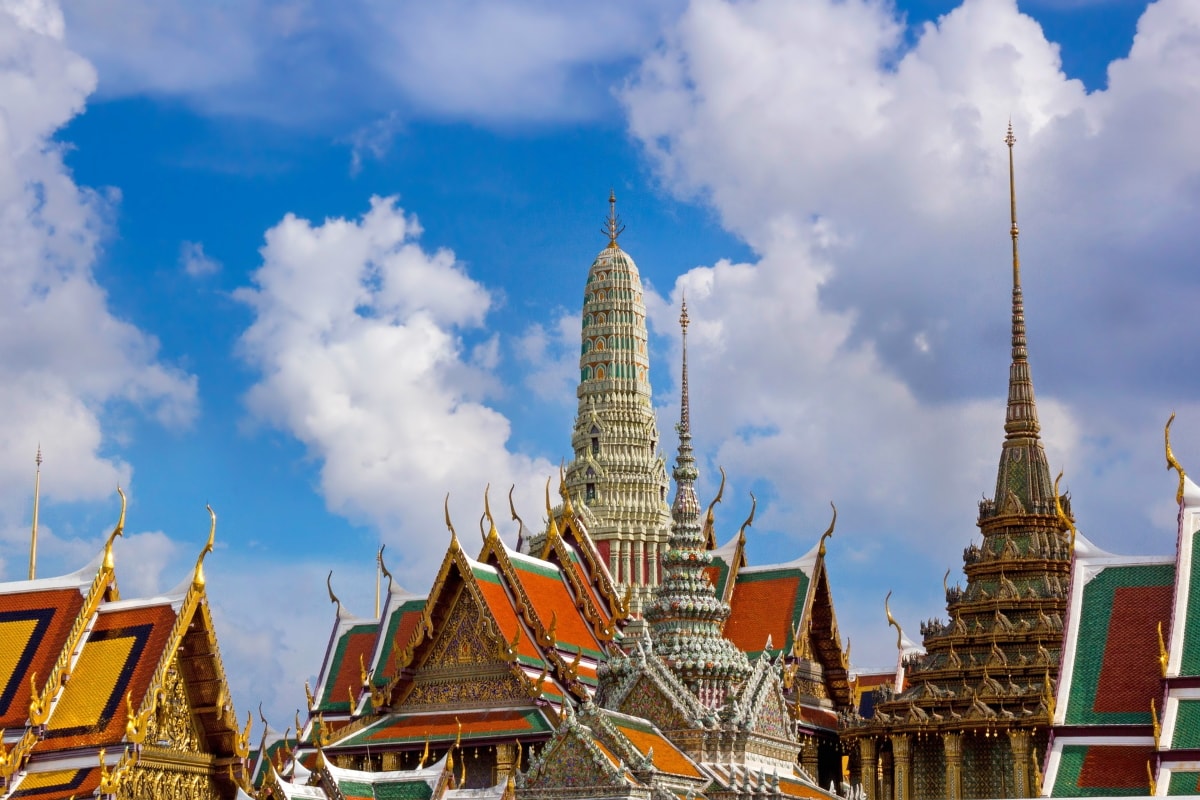
Thailand Economy
Thailand’s economy is the second-largest in southeast Asia and the eighth-largest in Asia. It is a newly-industrialised economy that depends heavily on exports.
In the last two decades, the economy of Thailand has grown at an average of 4%. Last year, Thailand’s nominal GDP expanded by 3.9% to $490 billion. The IMF predicts the Thai economy will grow at a rate of around 3.5 to 3.9% for the next five years.
Thailand: Upper-middle class with low unemployment
The Kingdom of Thailand had a population of over 69 million at the end of 2018. The population growth has been slowing since 2002, with an increase of only 0.2% last year.
According to the World Bank, Thailand has upgraded from a low-income economy to an upper-middle income society over the last four decades. In 2018, the country’s GDP per capita (PPP) reached $6,992.
Thailand’s unemployment rate is among the lowest in the world. Since 2011, the unemployment rate in Thailand has remained steady at just under 1%. Last year, only 0.7% of the population was jobless.
Currency and central bank
The Thai baht (฿ or Bt) is the official currency of Thailand. The official issuer of the Thai baht is the country’s central bank, Bank of Thailand (BOT). Established in 1942, BOT’s primary mission is to issue the currency and provide a stable financial environment for sustainable economic growth in the country. In March 2019, the central bank set the policy rate at 1.75%.
Thailand economy: Inflation rate
Thailand had an inflation rate of 0.5% in 2018. Since 2000, the BOT has applied a flexible inflation targeting regime. For 2019, the annual inflation target is set at 2.5% with 1.5% tolerance.
Industry and trade
The Thai economy is mostly driven by three sectors: services, industry and agriculture. The services sector contributes more than half of total GDP, followed by industry (39.2%) and agriculture (8.4%).
Other major industries in Thailand include automotive, electronics, financial services and tourism. The Thai automotive industry is the biggest in southeast Asia. The country is home to numerous car manufacturing plants, including BMW, Daihatsu, Ford and Honda.
Thailand is also one of the largest exporters of rice and shrimp in the world. Even though agriculture contributes less than one-tenth of total GDP, it plays an important role, as more than 30% of the labour force is employed in the sector.
More than 99% of companies in Thailand are categorised as small and medium-sized enterprises (SME’s). The country’s largest companies include oil and gas company PPT PCL, Kasikornbank, Siam Cement, and Thai Beverage.
Thailand Economy: Trade and Competitiveness
In 2018, Thailand recorded a trade surplus of $23.6 billion. Total exports reached $253.4 billion, while total imports were $229.8 billion. Thailand’s top trading partners both in exports and imports are China, Japan, and the U.S. ASEAN countries such as Malaysia, Singapore and Indonesia are also significant trading partners for the kingdom, bringing in over 30% of Thai exports. Manufacturing accounts for nearly 90% of Thailand total exports.
In 2018, Thailand received FDI inflows of $12.46 billion. This is up around 55% over the previous year. The biggest contributors were Japan, Hong Kong and Singapore. The manufacturing and financial sectors attract nearly 70% of total FDI inflows.
According to the World Bank, Thailand is ranked at 27th position in the ease of doing business index in 2019.
Stock exchanges and capital markets
The Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) is the main capital market of Thailand. Previously named the Securities Exchange of Thailand, it was established in 1974. As of March 2019, SET had 775 listed companies with a total market cap of more than $532 billion.
Main indices of the SET include the SET Index, SET50 Index and SET100 Index. These indices are market capitalisation-weighted price indices that track all the common stocks on the SET main board. SET also provides industry group indices, sectoral indices, and a Market for Alternative Investment (MAI) Index.
Thailand Economy: Stock Market Regulation
Foreign investors can buy the same stocks as local investors in the Stock Exchange of Thailand. However, according to the Foreign Business Act B.E. 2542 (1999), foreign shareholding in a Thai company is limited to between 25 to 49%. In a rescue situation, foreign investors may be allowed to be majority shareholders.
Once the foreign ownership threshold has been reached, a foreigner can purchase ‘Foreign Shares’ on the SET’s Foreign Board, which have different International Securities Identification Numbers (ISIN) than the local shares.










 Australia
Australia China
China India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Japan
Japan Malaysia
Malaysia Philippines
Philippines Singapore
Singapore South Korea
South Korea Taiwan
Taiwan Thailand
Thailand Vietnam
Vietnam Germany
Germany Hong Kong
Hong Kong USA
USA Switzerland
Switzerland Singapore
Singapore
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom














